Login / Logout pages Implementation 본문
Structure
- Users and the User Model
- Permissions
- Groups
- Passwords and Authentication
- Logging In and Out
1. Passwords
- General set-up to begin getting ready for User Authentication
- Some library options for security
1) Use some built-in apps and make sure they are under the INSTALLED_APPS list in settings.py
- You can pass in the list of PASSWORD_HASHERS to try in the order you want to try them
# setting.py
PASSWORD_HASHERS = [
'django.contrib.auth.hashers.PBKDF2PasswordHasher',
'django.contrib.auth.hashers.Argon2PasswordHasher',
'django.contrib.auth.hashers.BCryptSHA256PasswordHasher',
'django.contrib.auth.hashers.BCryptPasswordHasher',
'django.contrib.auth.hashers.PBKDF2SHA1PasswordHasher',
]
2) Django.contib.auth / Django.contrib.contenttypes
3) We need to migrate
4) Store our passwords safely – Never store passwords as plain text
- Using PBKDF2 algorithms / SHA256
- Bcrpyt and Argon2 – pip install bcrypt / pip install Django[argon2]
5) Add in validator options to prevent a user from making a very weak password.
AUTH_PASSWORD_VALIDATORS = [
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.UserAttributeSimilarityValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.MinimumLengthValidator',
'OPTIONS': {'min_length': 9}
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.CommonPasswordValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.NumericPasswordValidator',
},
]
6) Add some Folders – static / templates / media
# settings.py
TEMPLATE_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "templates")
STATIC_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'static')
MEDIA_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'media')
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS = [STATIC_DIR]
# MEDIA
MEDIA_ROOT = MEDIA_DIR
MEDIA_URL = '/media/'
2. Use Django’s built in tools to create User Authorization Models.
- User object – is_active, is_staff, is_superuser
How to set-up media file in your project.
Imaging Library need to work with images with Python
- Pip install pillow
- Pip install pillow –gloabal-option=”build_ext” –global-option=”—disable-jpeg”
Register admin.py file
- Admin.site.register(UserProfileInfo)
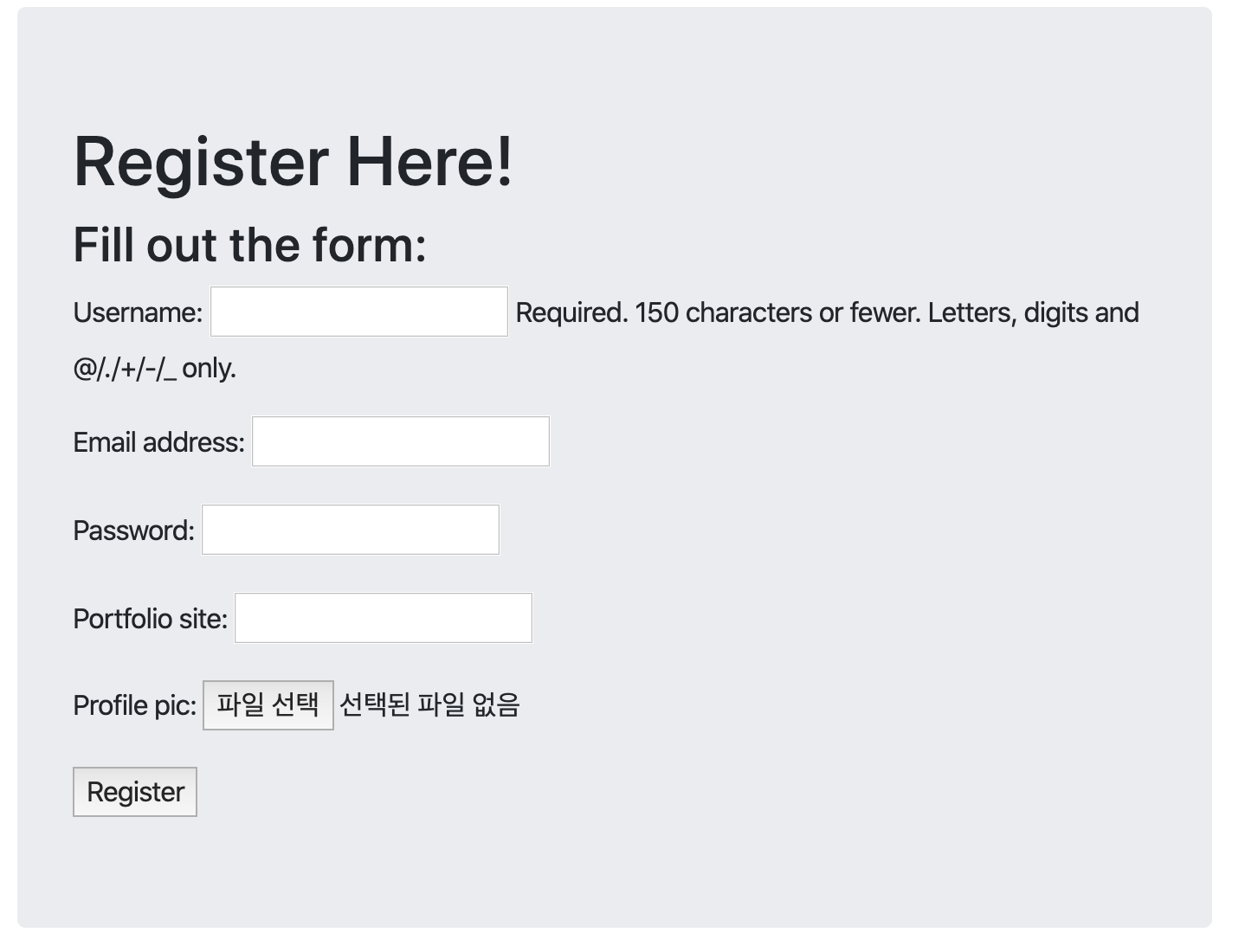
User Model / Media Directory / Handling Images / User Form
# models.py
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
# Create your models here.
class UserProfileInfo(models.Model):
# Create relationship (don't inherit from User!)
user = models.OneToOneField(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
# Add any additional arributes you want
portfolio_site = models.URLField(blank=True)
profile_pic = models.ImageField(upload_to='profile_pics', blank=True)
def __str__(self):
# Built-in attribute of django.contrib.auth.model.User!
return self.user.username
# forms.py
from django import forms
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from basic_app.models import UserProfileInfo
class UserForm(forms.ModelForm):
password = forms.CharField(widget=forms.PasswordInput())
class Meta():
model = User
fields = ('username', 'email', 'password')
class UserProfileInfoForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta():
model = UserProfileInfo
fields = ('portfolio_site', 'profile_pic')
# admin.py
from django.contrib import admin
from basic_app.models import UserProfileInfo
# Register your models here.
admin.site.register(UserProfileInfo)
# templates/basic_app/html files
# base.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" dir="ltr">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Base</title>
<-- Download the bootstrap -->
</head>
<body>
<nav class="navbar navbar-default navbar-static-top">
<div class="container">
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
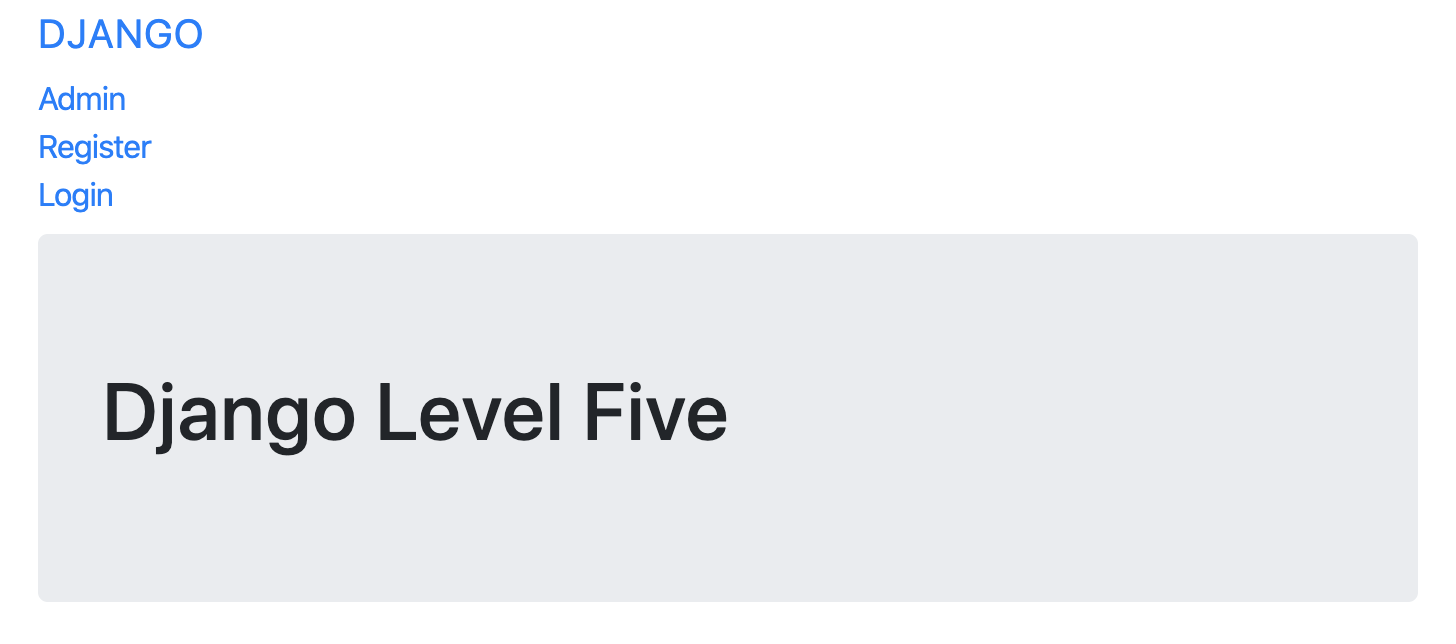
<li><a class="navbar-brand" href="{% url 'index' %}">DJANGO</a></li>
<li><a class="navbar-link" href="{% url 'admin:index' %}">Admin</a></li>
<li><a class="navbar-link" href="{% url 'basic_app:register'%}">Register</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</nav>
<div class="container">
{% block body_block %}
{% endblock %}
</div>
</body>
</html>
# index.html
{% extends "basic_app/base.html" %}
{% block body_block %}
<div class="jumbotron">
<h1>Django Level Five</h1>
</div>
{% endblock %}
# registration.html
{% extends "basic_app/base.html" %}
{% block body_block %}
<div class="jumbotron">
<h1>Django Level Five</h1>
</div>
{% endblock %}
# urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
from basic_app import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', views.index, name='index'),
path('basic_app/', include('basic_app.urls'))
]
# basic_app/urls.py
from django.urls import path
from basic_app import views
# TEMPLATE URLS!
app_name = 'basic_app'
urlpatterns = [
path('register/', views.register, name='register')
]
3. Registration
A lot of the coding for working with Users and Authorization happens in the views.py file.
If there is a POST request and then perform some sort of action based off that information.
Sometimes we’ll want to save that information directly to the database. Other times, we’ll set commit=False so we can manipulate the data before saving it to the database.
- This helps prevent collision errors.
# views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from basic_app.forms import UserForm, UserProfileInfoForm
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
return render(request, 'basic_app/index.html')
def register(request):
registered = False
if request.method == "POST":
user_form = UserForm(data=request.POST)
profile_form = UserProfileInfoForm(data=request.POST)
if user_form.is_valid() and profile_form.is_valid():
user = user_form.save()
user.set_password(user.password)
user.save()
profile = profile_form.save(commit=False)
profile.user = user
if 'profile_pic' in request.FILES:
profile.profile_pic = request.FILES['profile_pic']
profile.save()
registered = True
else:
print(user_form.errors, profile_form.errors)
else:
user_form = UserForm()
profile_form = UserProfileInfoForm()
return render(request, 'basic_app/registraion.html', {'user_form': user_form, 'profile_form': profile_form, 'registered': registered})
4. Logins
- Setting up the login views
- Using built-in decorators for access
- Adding the LOGIN_URL in settings
- Creating the login.html
- Editing the urls.py file
# setting.py
# LOGIN
LOGIN_URL = '/basic_app/user_login'
# login.html
{% extends 'basic_app/base.html' %}
{% block body_block %}
<div class="jumbotron">
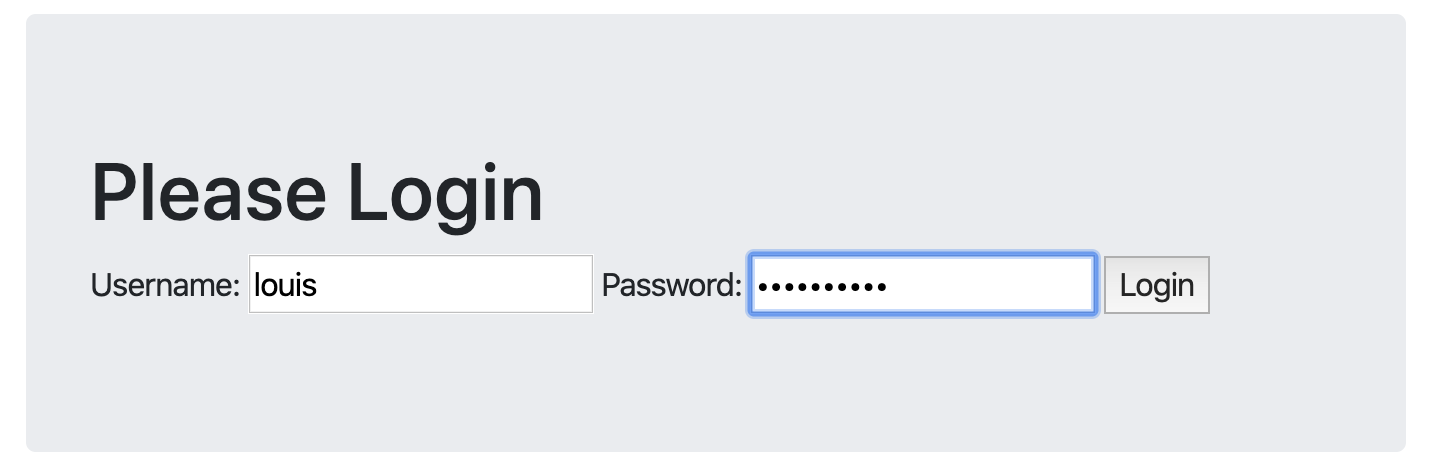
<h1>Please Login</h1>
<form action="{% url 'basic_app:user_login' %}" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="Enter Username">
<label for="password">Password:</label>
<input type="password" name="password">
<input type="submit" name="" value="Login">
</form>
</div>
{% endblock %}
# views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from basic_app.forms import UserForm, UserProfileInfoForm
#
from django.contrib.auth import authenticate, login, logout
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect, HttpResponse
from django.urls import reverse
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import login_required
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
return render(request, 'basic_app/index.html')
@login_required
def special(request):
return HttpResponse("You are logged in, Nice!")
@login_required
def user_logout(request):
logout(request)
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('index'))
def register(request):
registered = False
if request.method == "POST":
user_form = UserForm(data=request.POST)
profile_form = UserProfileInfoForm(data=request.POST)
if user_form.is_valid() and profile_form.is_valid():
user = user_form.save()
user.set_password(user.password)
user.save()
profile = profile_form.save(commit=False)
profile.user = user
if 'profile_pic' in request.FILES:
profile.profile_pic = request.FILES['profile_pic']
profile.save()
registered = True
else:
print(user_form.errors, profile_form.errors)
else:
user_form = UserForm()
profile_form = UserProfileInfoForm()
return render(request, 'basic_app/registration.html', {'user_form': user_form, 'profile_form': profile_form, 'registered': registered})
def user_login(request):
if request.method == "POST":
# Same with login.html input name
username = request.POST.get('username')
password = request.POST.get('password')
user = authenticate(username=username, password=password)
if user:
if user.is_active:
login(request, user)
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('index'))
else:
return HttpResponse("ACCOUNT NOT ACTIVE")
else:
print("Someone tried to login and failed!")
print("Username: {} and password {}".format(username, password))
return HttpResponse("Invalid Login details supplied!")
else:
return render(request, 'basic_app/login.html', {})
# urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
from basic_app import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', views.index, name='index'),
path('basic_app/', include('basic_app.urls')),
path('logout/', views.user_logout, name='logout'),
path('special/', views.special, name='special')
]
# app/urls.py
from django.urls import path
from basic_app import views
# TEMPLATE URLS!
app_name = 'basic_app'
urlpatterns = [
path('register/', views.register, name='register'),
path('user_login/', views.user_login, name='user_login')
]
'개발 > Django' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CBV (Class Based Views) (0) | 2020.05.13 |
|---|---|
| Django Deployment (0) | 2020.05.13 |
| Templates - Relative URLs+ Inheritance + Filter (0) | 2020.05.07 |
| 장고 공부법 (0) | 2020.05.07 |
| Data List on the web page (0) | 2020.05.05 |


